High Resolution Polar Kerr Effect Studies of CsV3Sb5
Published in PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS, 2023
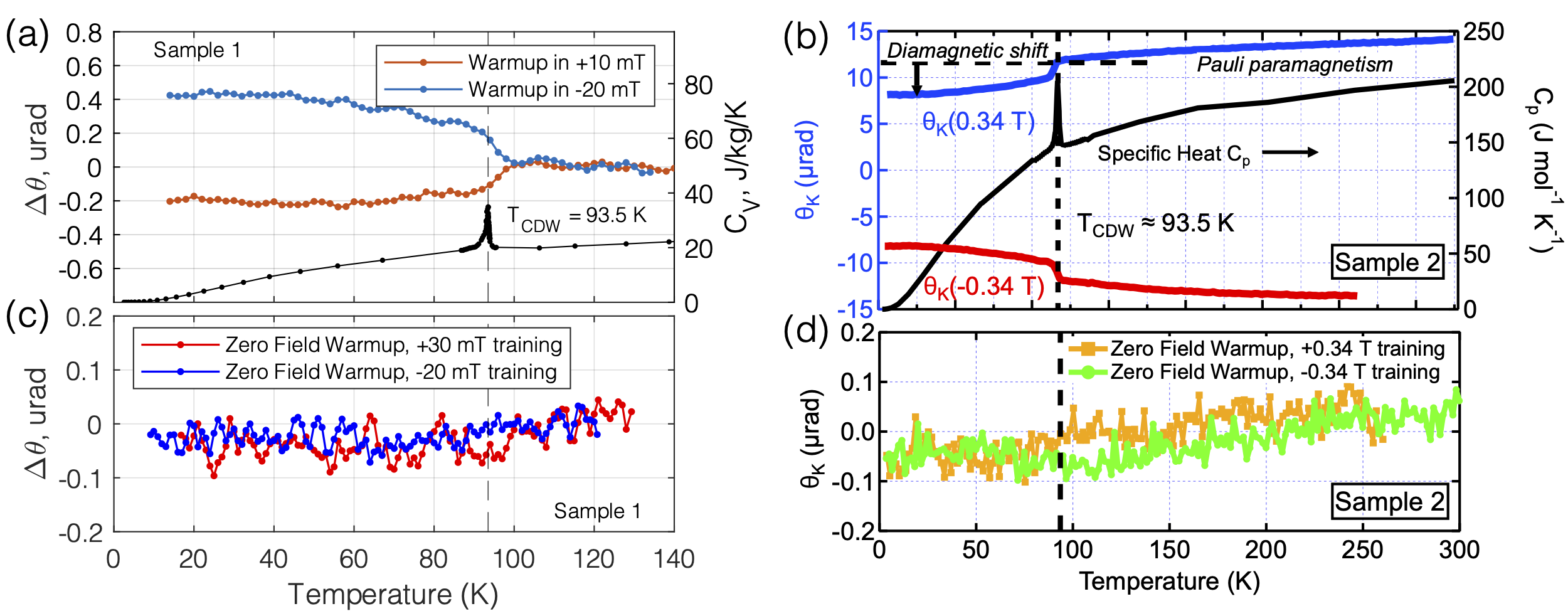
We report high resolution polar Kerr effect measurements on CsV3Sb5 single crystals in search of signatures of spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking below the charge-order transition at \(T_{*}\) = 94 K. Utilizing two different versions of zero-area loop Sagnac interferometers operating at 1550 nm wavelength, each with the fundamental attribute that without a time-reversal symmetry breaking sample at its path, the interferometer is perfectly reciprocal, we find no observable Kerr effect to within the noise floor limit of the apparatus at 30 nanoradians. Simultaneous coherent reflection ratio measurements confirm the sharpness of the charge-order transition in the same optical volume as the Kerr measurements. At finite magnetic field we observe a sharp onset of a diamagnetic shift in the Kerr signal at \(T_{*}\), which persists down to the lowest temperature without change in trend. Since 1550 nm is an energy that was shown to capture all features of the optical properties of the material that interact with the charge-order transition, we are led to conclude that it is highly unlikely that time-reversal symmetry is broken in the charge ordered state in CsV3Sb5.